
As much as 65-70% of women with PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) struggle with insulin resistance (source). This means that addressing insulin resistance is key for improving PCOS symptoms. That’s why this post explores the use of inositol vs berberine for PCOS.
Do they live up to the hype? And, how do they weigh-up against each other?
We’ll answer these questions so you can make the best choice for you. You’ll learn the benefits of inositol and berberine, how to take them, and any side effects.
NOTE: This post contains affiliate links and I earn a commission (at no additional cost to you) if you use them to make a purchase.
BENEFITS OF INOSITOL FOR PCOS
There are 9 different types of inositol, though not all are relevant for PCOS.
Of these, myo-inositol (MI) and d-chiro-inositol (DCI) prove effective for treating PCOS.
In the body, these separate forms of inositol have a slightly different effect.
MI is utilized in tissues that require higher amounts of glucose such as the heart, brain, and ovaries.
As for DCI, it gathers in areas of glucose storage such as the muscles and liver (which is essential for hormone balance as discussed here).
These are significant benefits if you have PCOS.
So now you know the basics, let’s further explore the main benefit of inositol.
1. Insulin Sensitizer
The main reason Inositol is used as a supplement for PCOS is because it increases insulin sensitivity. Let’s break down this insulin-sensitizing process.
Our cell walls contain an abundance of a glycolipid called phosphatidyl-myo-inositol.
This is a precursor to inositol triphosphate (also known as InsP3)—which acts as a signaling molecule—relaying information between the different cells of your body.
InsP3 regulates the activity of other hormones. Specifically:
- Insulin
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Serotonin
Complications arise when the InsP3 pathway malfunctions, which can then have a negative impact on all of the hormones listed above.
In particular, any issues in the InsP3 pathway can cause issues related to insulin signaling, and that increases the chances of insulin resistance occurring.
So, by using a supplement like inositol, you may see improvements in various aspects of your health, including:
- blood sugar levels.
- insulin function.
- reproductive health and ovarian function.
- improvements in mood and sleep.
2. May Lower Androgen Levels
According to a small study conducted with 20 lean PCOS patients, D-chiro inositol lowered free testosterone by 73% (compared to the placebo group, which had no changes).
In another study, 50 PCOS patients were given myo-inositol for 6 months. At the 3-month mark, they researchers found that total testosterone and free testosterone had reduced. And by the 6-month mark, they noticed a decrease in acne and hirsutism (source).
Furthermore, a study conducted with 42 PCOS patients, the researchers compared the effects of myo-inositol and folic acid versus folic acid alone (source).
The results showed that the group taking myo-inositol and folic acid had a more significant decrease in total testosterone and free testosterone levels (compared to the group taking folic acid alone).
So, based on these studies, inositol looks like a promising remedy for elevated androgen.
3. May Restore Ovulation and Support Fertility
One study found that 60% of women taking D-chiro inositol ovulated compared to only 20% of women who were taking a placebo.
In addition, a review of 197 medical articles about inositol confirmed that many studies have shown inositol to be beneficial for ovulation and fertility (source).
BENEFITS OF BERBERINE FOR PCOS

Berberine is a bioactive chemical compound found in herbs, such as:
- Goldenseal.
- Oregon grape.
- Barberry.
It’s capable of influencing the body at a molecular level, producing various, profound health benefits.
Below we’ll examine some of the scientifically backed benefits associated with this plant alkaloid.
1. Insulin Sensitizer
Like inositol, berberine acts as an insulin sensitizer.
In 2012, a study concluded that berberine was as effective as metformin at lowering insulin—but with fewer side effects (source).
In that study, 89 women with PCOS were split into 3 groups, where they took one of the following:
- 500mg berberine, three times a day.
- 500mg metformin, three times a day.
- A placebo for three months.
In addition to this, they were instructed to reduce fats and carbs, and to do moderate to high-intensity exercise for 30 minutes a day.
After 3 months, the group taking berberine had a more significant reduction in body fat. In addition, their insulin levels improved and they had fewer side effects compared to the group taking metformin.
2. May Lower Androgen Levels
Androgens are a group of sex hormones that regulate male characteristics. Women with PCOS produce about 20x more androgens from their ovarian theca cells than other women (source).
This hormonal excess may manifest as acne, hair thinning, or facial and body hair growth.
However, there are several encouraging studies—conducted with both mice and women—that confirm berberine’s ability to lower these elevated androgen levels.
At this point, these studies can only theorize how berberine produces this effect. Some studies believe it must suppress androgen receptor signaling through a direct action on the ovaries.
Others suggest the herbal compound works through increasing SHBG (sex hormone binding globulin) levels. As the name suggests, SHBG binds to sex hormones, specifically: estradiol, testosterone and DHT.
Yet, SHBG tends to be low in PCOS patients—likely because of insulin resistance. This results in more available, unattached androgens in the system and causes too much testosterone to go to bodily tissue.
3. May Support Reproduction and Fertility
A major symptom of PCOS are issues with fertility and reproduction.
Women with PCOS experience ongoing hormonal imbalances that disrupt ovulation (and if there’s no egg, there’s no possibility of conception).
Thankfully, berberine can help with this too.
Studies have shown a 25% improvement in ovulation for 98 PCOS patients—who experienced anovulation—after taking berberine for four months (source).
These women also showed higher pregnancy rates when they took berberine, in comparison with other control groups who took metformin or a placebo.
Overall, berberine showed great potential for supporting healthy ovulation patterns and increasing live birth rates.
4. May Reduce Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Although we typically associate fatty liver disease with people who drink excessive amounts of alcohol, women with PCOS can develop a non-alcoholic form of the disease.
The symptoms that occur with PCOS help create a “perfect storm” for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Insulin resistance, excess weight, and excess androgens can all contribute to its development.
Yet, extensive studies have shown how berberine can help NAFLD.
For example, 500 people took part in six randomized control trials with the aim to show how berberine could impact NAFLD symptoms.
The results?
- Lower liver function enzymes
- Lower triglycerides
- Improved liver functioning
- Promotion of fatty acid oxidation and the break-down of fatty acids
- Prevention of liver fat build-up (source).
After these outcomes it’s hard to deny berberine’s potential therapeutic value.
HOW TO TAKE BERBERINE AND INOSITOL FOR PCOS
Since both inositol and berberine are beneficial for PCOS, let’s look at how to get the most from them.
First, inositol.
- For optimal results you need to combine myo-inositol and d-chiro-inositol. Studies show these compounds produce a powerful synergistic effect that is ideal for managing PCOS (source).
- The key to success involves ratio. A 40:1 (MI to DCI) ratio has been shown to be most helpful for ovarian function and overall improvement of PCOS symptoms.
- Research shows that changing this ratio produced less effective results, leading the researchers to conclude that increasing DCI minimized reproductive benefits (source).
- Researchers drew similar conclusions in other studies. Deviation from this ratio wasn’t as effective and could even have a negative effect. This was the case when a 5:1 (MI to DCI) ratio was used in place of 40:1 (source).
- Most store-bought inositol products adhere to this optimal 40:1 ratio. To guarantee you’re getting this ratio you’ll need to check the label. This would work out to 2000mg of myo-inositol for every 50mg of d-chiro-inositol.
Now, let’s look at how to take berberine.
- Unfortunately, there’s no conclusive berberine dosage recommendation for PCOS. Studies have confirmed berberine is safe and promising for PCOS management, though they emphasize more research is required for specific dosing advice (source).
- Studies done on berberine have used different doses ranging from 500-1500mg per day.
- Because there is no definitive dosage, you’re better off consulting your healthcare provider so that they can instruct you on appropriate dosing.
HOW LONG TO TAKE BERBERINE OR INOSITOL
Neither inositol nor berberine are meant to be used perpetually. On average, studies show an improvement in symptoms around the 3-month mark.
For inositol supplementation, no one knows if it can be used long-term. So far studies at looked at the use of inositol for about 12 months, but nothing beyond part.
As for berberine, research shows it is not supposed to be a long-term supplement.
So, whichever supplement you use, it’s important to make diet and lifestyle changes to support your body long term.
BEST BERBERINE AND INOSITOL SUPPLEMENT FOR PCOS
1. Ovasitol
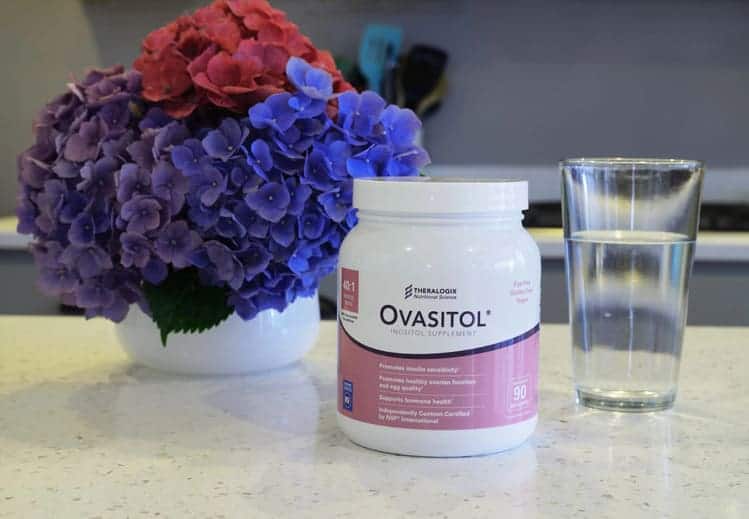

This is one of the most popular inositol supplements because it contains myo and D-chiro inositol.
It’s a powder and comes as a 90-day supply which is very convenient since it can take about 90 days for inositol to work.
By purchasing directly from the manufacturer you also get a discounted (PRC) price since I’m an affiliate for them.
Get Ovasitol here at a discounted price.
2. Berberine from Integrative Therapeutics

This is a straightforward supplement that provides 500 mg of berberine in each capsule. Simple and gives you exactly what you need.
SIDE EFFECTS OF INOSITOL AND BERBERINE
While there is no recommended daily allowance (RDA) for inositol, there is still a limit for how much you should take. High doses – about 12 grams a day – may cause gastrointestinal-related issues like gas, nausea, or diarrhea (source).
Similar to inositol, berberine can also cause digestive disturbances like gas, diarrhea, or constipation.
CAN YOU TAKE BERBERINE AND MYO-INOSITOL TOGETHER?
Avoid the temptation to take berberine and inositol together. They’re both insulin sensitizers, so taking both simultaneously could drastically lower blood sugar levels.
This also applies to other supplements or medications that lower blood sugar, such as N-acetylcysteine or metformin.
As always, check with your healthcare provider before adding a new product into your routine. This will ensure you get the most from these products and minimize potential side-effects.
CONCLUSION
Both inositol and berberine may help to address insulin resistance, elevated androgen levels and other symptoms of PCOS.
Therefore it’s worth considering whether they’re a good fit for you. However, neither supplement is considered a magical fix.
So, it’s best to use these exactly as they’re intended: as a supplement or add-on to a PCOS-friendly diet and lifestyle (which you can learn more about here).
In addition, it’s always best to work with your healthcare provider so that you can get a customized dosage for these supplements.

Related Articles:
Inositol For PCOS: Pros, Cons and Food Sources
Vitex vs Inositol: Benefits | Differences | Which is Better for PCOS and More
Hormone Balancing Foods for PCOS: A Complete Guide (with PDF)
The Truth About Apple Cider Vinegar for PCOS


